Polyethylene is one of the most widely used polymers in the world and is extensively utilized in various industries. This material, derived from petroleum products, is highly valued for its unique properties, such as moisture resistance, high flexibility, and recyclability, making it ideal for producing various plastic products, including packaging, pipes, and household items.
As one of the most widely used and versatile polymers globally, polyethylene plays a vital role in many industries. From packaging and piping to agriculture and automotive manufacturing, this material’s unique properties, including moisture resistance, flexibility, chemical resistance, and recyclability, make it a go-to choice for countless applications. With increasing attention to environmental sustainability and the need to reduce raw material consumption, the use of recycled polyethylene is expected to grow significantly in the future.
History of Polyethylene
Polyethylene was first discovered in 1898 by the German chemist Hans von Pechmann by accident. While decomposing diazomethane, he noticed the formation of a waxy substance at the bottom of a test tube. This material was later identified as polyethylene. However, polyethylene was not commercially produced until the 1930s. The first industrial production of this polymer took place in 1933 by the British company Imperial Chemical Industries (ICI). Since then, polyethylene has become one of the most important plastics used across many industries.

Types of Polyethylene
Polyethylene can be classified into different types based on molecular structure and density, each having specific properties and applications:
High-Density Polyethylene (HDPE) : High-Density Polyethylene (HDPE) is a linear polymer with very few side branches. This linear structure gives HDPE superior mechanical properties, such as higher resistance to pressure and impact. As a result, HDPE is used for manufacturing products like water pipes, fuel tanks, and containers for chemical storage. HDPE also has excellent moisture and chemical resistance.
Low-Density Polyethylene (LDPE) : Low-Density Polyethylene (LDPE) has a highly branched structure, which provides greater flexibility. LDPE is mainly used for producing plastic films, such as nylon bags, plastic bags, food packaging, and certain household items. While LDPE has lower mechanical strength than HDPE, it is more suitable for applications requiring higher flexibility.
Linear Low-Density Polyethylene (LLDPE) : Linear Low-Density Polyethylene (LLDPE) is a polymer with properties between HDPE and LDPE. This type of polyethylene is commonly used in producing plastic films and flexible packaging. LLDPE offers better resistance to tearing and stretching, and due to its more linear structure compared to LDPE, it performs better in certain industrial applications.
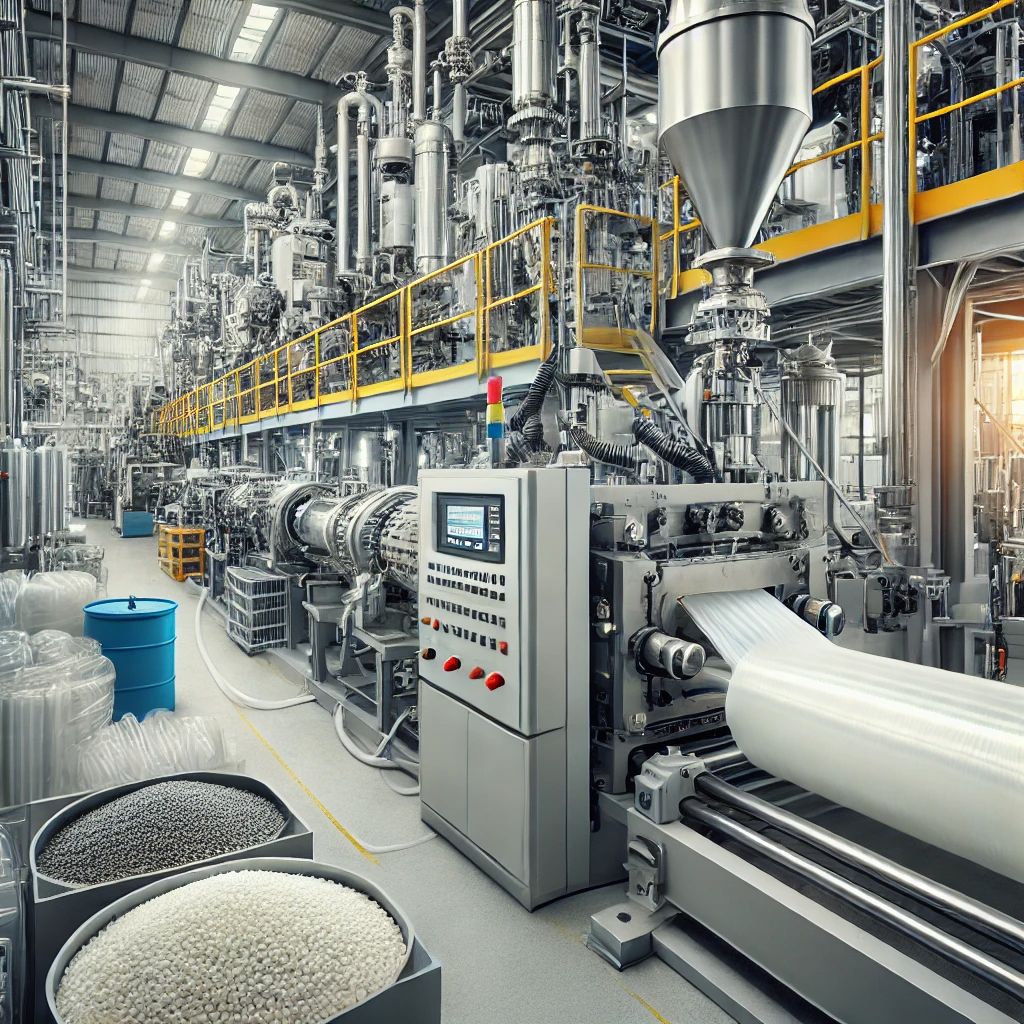

Advantages of Polyethylene
Polyethylene’s outstanding characteristics make it one of the most popular plastics worldwide. Some of its advantages are as follows:
High Moisture Resistance
One of the prominent features of polyethylene is its excellent resistance to moisture. This makes it ideal for packaging food and moisture-sensitive products. Polyethylene is also widely used in water piping and liquid transportation systems.

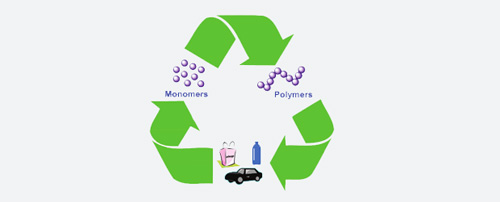
Recyclability
Polyethylene is one of the most easily recyclable plastics. This makes it environmentally friendlier compared to other types of plastics. Recycling polyethylene helps in the production of new products and reduces the need for raw materials.
Flexibility and Mechanical Strength
Polyethylene is highly flexible and can resist impact and pressure. This property makes it suitable for manufacturing various products, including plastic bags, packaging films, and industrial pipes.

Chemical Resistance
Polyethylene has excellent resistance to many chemicals. Therefore, it is used to produce chemical storage tanks and pipes that transport corrosive substances. This chemical resistance makes polyethylene widely applicable in chemical, petrochemical, and pharmaceutical industries.
Applications of Polyethylene
Polyethylene has widespread applications in various industries, and here are some of the most important ones:
1. Packaging
One of the primary uses of polyethylene is in the packaging industry. Due to its flexibility, moisture and chemical resistance, and recyclability, polyethylene is used to produce plastic packaging such as bags, films, and bottles.
2. Piping
Polyethylene is one of the best materials for manufacturing pipes used in water, gas, and chemical transportation. Polyethylene pipes are resistant to corrosion, pressure, and impact and have a long lifespan, making them suitable for piping systems.
3. Agriculture
In agriculture, polyethylene is used to produce greenhouse films, irrigation pipes, and plant protection covers. These products help improve efficiency and productivity in agriculture.
4. Automotive Industry
In the automotive industry, polyethylene is used to produce various parts, including fuel tanks, cooling system pipes, and some interior car components. Its resistance to chemicals and high mechanical properties make polyethylene suitable for numerous automotive applications.

