Polymeric materials are a class of substances composed of long molecular chains known as polymers. These materials are widely used across various industries due to their unique properties. From packaging and consumer products to industrial and medical components, polymeric materials play a key role in everyday human life. In this article, we will explore the definition, types, properties, and applications of polymeric materials.
Due to their structural diversity and unique physical and chemical properties, polymeric materials hold a special place in many industries. From everyday applications like packaging and household products to advanced uses in industries like medicine and aerospace, polymers are indispensable thanks to their many advantages. As technology advances and the demand for high-performance and environmentally friendly materials grows, further innovations in the field of polymeric materials are expected.
Definition of Polymer
Polymers are large molecules made up of repeating smaller units called monomers. These monomers can bond together in long chains to form polymeric materials. The word “polymer” is derived from the Greek words “poly” meaning “many” and “mer” meaning “unit,” essentially meaning “many units.”
Polymeric materials can be either natural or synthetic. Natural polymers include substances like proteins, starch, and cellulose, which are found in the structure of living organisms and plants. On the other hand, synthetic polymers are produced through chemical processes in various industries.

Types of Polymeric Materials
Polymeric materials are classified into different types based on their chemical structure, physical properties, and production processes. Here are some of the most important categories:
Thermoplastics: Thermoplastics are materials that soften when heated and can be molded into different shapes. Once cooled, they solidify again and can be melted and reshaped multiple times. Common thermoplastics include polyethylene, polypropylene, polystyrene, and polyvinyl chloride (PVC). These materials are widely used in various industries such as packaging, automotive, and electronics due to their recyclability and flexibility.
Thermosets : Unlike thermoplastics, thermosets cannot be remelted once they have been cured and shaped. These materials become permanently solid after undergoing a heating and curing process. Examples of thermosets include epoxy resins, polyesters, and polyurethanes. Thermosets are used in applications requiring high resistance to heat and pressure, such as aerospace, automotive parts, and electrical equipment.
Elastomers : Elastomers are highly flexible polymeric materials that return to their original shape after being stretched. Natural and synthetic rubber are examples of elastomers. These materials are used in the production of tires, gaskets, rubber bands, and products related to transportation and sports due to their elasticity and high resistance to deformation.

Properties of Polymeric Materials
Polymeric materials possess unique properties that distinguish them from other materials like metals and ceramics. Here are some key characteristics:
Lightweight
One of the standout features of polymeric materials is their lightweight nature compared to metals and ceramics. This is especially beneficial in industries such as automotive and aerospace, where reducing the weight of products is crucial.
Chemical Resistance
Polymeric materials usually exhibit good resistance to chemicals such as acids, bases, and solvents. This makes them ideal for applications involving the storage and transportation of chemicals and pharmaceuticals.
Flexibility
Polymers vary in their degree of flexibility. Some are soft and pliable, while others are more rigid and strong. This range of flexibility allows polymers to be used in a wide variety of products.

Recyclability
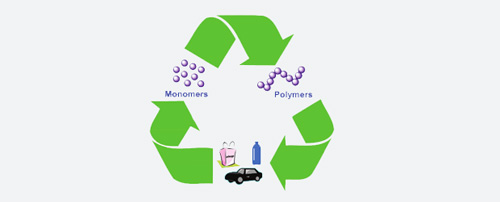
Many polymers, particularly thermoplastics, are recyclable. This allows these materials to be reused in production and consumption cycles, reducing their negative environmental impact.
Applications of Polymeric Materials
Due to their diversity and specific properties, polymeric materials are used extensively in various industries. Below are some of the major applications:
1. Packaging Industry
One of the primary uses of polymeric materials is in the packaging industry. Due to their lightweight, flexibility, and resistance to moisture and chemicals, polymers are used to produce plastic packaging such as bags, bottles, and packaging films.
2. Automotive Industry
In the automotive industry, polymeric materials are used to manufacture both interior and exterior vehicle components, such as dashboards, bumpers, and seats, due to their lightweight and resistance to corrosion and wear. These materials help reduce vehicle weight and improve fuel efficiency.
3. Medical Industry
Polymeric materials play a significant role in the medical industry. Many medical devices, such as syringes, disposable gloves, medical tubing, and blood bags, are made from various polymers. In addition, polymers are used in the production of implants and body prosthetics.
4. Construction Industry
In construction, polymeric materials are used due to their durability and resistance to environmental conditions. These materials are employed in the production of water and sewage pipes, thermal and sound insulation, and various building components. Polymers are also used to produce PVC windows, flooring, and wall coverings.

